Introduction
Entrepreneurship is the backbone of any economy, driving innovation and employment. Governments and organizations provide various incentives to entrepreneurs to reinforce this spirit. These incentives act as motivators, helping candidates overcome challenges and succeed. This article explores the types of incentives available, their importance, and how they help entrepreneurs.
Meaning of Incentives to Entrepreneurs

Entrepreneurs in India are offered several incentives because they fulfill two main objectives of economic development. Firstly, they facilitate decentralisation of industries They take up new ventures even in rural areas.
The term ‘Incentive’ means stimuli for action. The stimuli motivate entrepreneurs to start and run small-scale industrial units. Motivation is like a push that makes people want to work harder and do their jobs better. They are like the helping hand of government to businesses, especially in areas that need a little extra help to grow.
It’s all about motivation leading to excellent decision-making, and choosing the right option based on independent abilities is the driving force that carries an entrepreneur through.
The government provides economic development assistance to businesses to help them grow in various sectors, especially in less developed areas. This support encourages entrepreneurs to make smart choices and rely on their skills to succeed.
The purpose of incentives is to bring an entrepreneur into undertaking new ventures, which will contribute to wider public benefit at both national and societal levels. Incentives include concessions, subsidies, and bounties.
Importance or Advantages of Incentives to Entrepreneurs
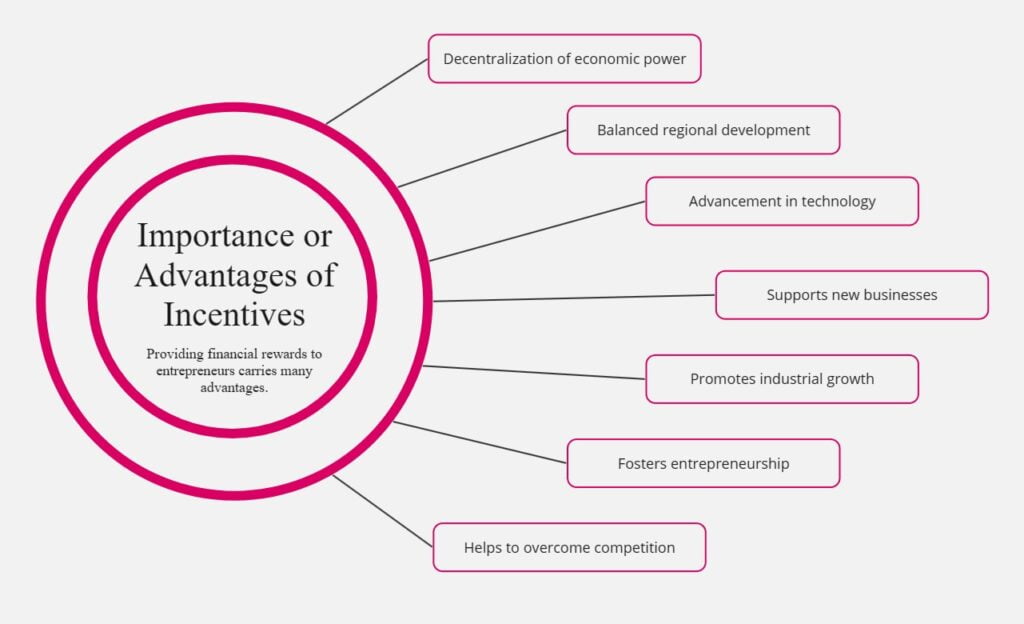
Providing financial rewards to entrepreneurs carries many advantages.
- Decentralization of economic power: Indicative mechanisms are designed to motivate novice entrepreneurs to engage in manufacturing business. It, in turn, enables people to get hold of economic power, which is decentralized in society.
- Balanced regional development: In our country, there is an imbalance in development across different regions. Some are well-developed and some are underdeveloped. We also want to componentize entrepreneurs who are opening business entities in underdeveloped areas by providing rewarding tools. It will result in the geographical expansion of primary business sectors along the country. Thus, this contributes to regional balanced development.
- Advancement in technology: Rewards are not only the drivers but also the supporters for changing the traditional industries into new industries. Traditional technology is characterized by low skill, low productivity, and low wages, whereas modern technology is characterized by improved skills, high productivity, higher wages, and a higher standard of living.
- Supports new businesses: The incentives and concessions package made up of free land, discounted raw materials like power, low taxes, and business registrations is for the entrepreneurs to go to less developed areas and establish a unit there. One way these advantages can be tackled is through society addressing the underlying problems in the regions.
- Promotes industrial growth: The creation of such incentives is designed to correct market defects and quicken industrialization. To create a development pattern that will lead to an imbalanced economy, the leadership must have a sense of balance for the proper utilization of resources and reduction of income gaps.
- Fosters entrepreneurship: Small business proprietors often fail because of the poor support system and talents included in starting a business. Government assistance in subsidies and concessions provides a sustainable environment for new ventures to co-compete in the market. Thus, subsidies and incentives promote entrepreneurship in the country by removing economic constraints.
- Helps to overcome competition: In this competitive world, small-scale enterprises established by entrepreneurs face stiff competition from big firms. If a business doesn’t receive the required public support they won’t be able to stand on their foot and survive the competition. Thus certain incentives are required. For example, reservation policy, price preference, preferential purchase, etc., help to improve the competitive strength of small-scale enterprises.
The Hidden Downsides of Over-Incentives Entrepreneurs
- Dependency on Rewards: When incentives are given in excess, it can create a reliance on external rewards. Instead of focusing on building a sustainable business fueled by their own motivation for innovation and growth, entrepreneurs become fixated on chasing after handouts. This obsession hampers creativity and leads to making short-sighted decisions, favoring immediate gains rather than long-term vision.
- Unsustainable Practices: The pursuit of incentives can result in the adoption of unsustainable business models. Entrepreneurs may resort to cutting corners or prioritizing activities that maximize incentive fulfillment, disregarding the development of a value-driven company in the long run. This can lead to ethical breaches and practices that ultimately harm the business itself.
- Distorted Market Competition: Programs with heavy incentives can distort the competition within the market. Established entrepreneurs, who rely less on handouts and prioritize building a strong product or service, can be unfairly disadvantaged by those who prioritize chasing incentives. This creates an uneven playing field and discourages the organic growth of innovative ideas.
Need for Incentives to Entrepreneurs
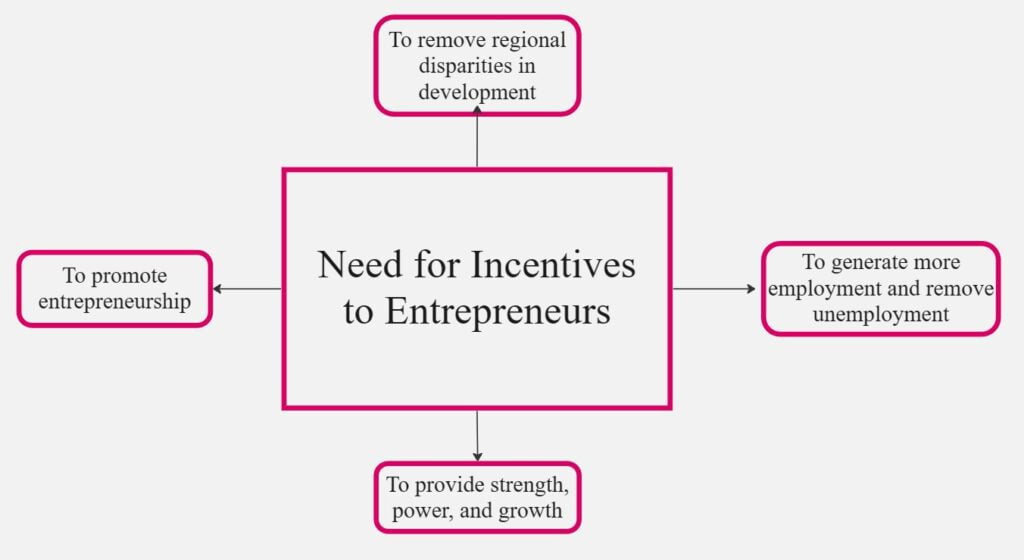
The question of privileges and subsidies considers a variety of aspects.
- To remove regional disparities in development: Industries may be concentrated and overcrowded in some regions while backward regions may remain backward without many industries. Encouraging entrepreneurs will end the imbalance in the regional distribution of wealth. They will go ahead with the projects to start new corporations in those lesser-developed areas. In the long run, a backward region tends to be developed, and therefore that regional imbalance is eliminated.
- To promote entrepreneurship: The new entrepreneurs may face several problems on account of inadequate infrastructural facilities, marketing assistance, other institutional services, etc. All these problems may discourage them. However, the various incentives minimize some or all of the problems. One of the most effective forms of subsidies is the creation of industrial parks, affordability of electricity, concessional finance, capital investment subsidy, transport subsidy, etc, which are designed to tempt entrepreneurs to invest in new businesses. Thus, incentives are meant to promote entrepreneurship in a country.
- To provide strength, power, and growth: One of the most effective forms of subsidies is the creation of industrial parks, affordability of electricity, concessional finance, capital investment subsidy, transport su, subsidy, etc, which are designed to tempt entrepreneurs to invest in new businesses. For example, reservation of products, price preference, etc., will improve the competitive strength. Other benefits like low-interest loans, tax breaks, etc., help them prosper and expand.
- To generate more employment and remove unemployment: The proper use of incentives and subsidies will generate more employment by accelerating industrial growth. As disadvantages of a country, competition in itself and external economies cause some changes. Subsidies to businessmen to emphasize the movement from advanced areas to those considered developing or those moving backward in the region. Emphasized in a nutshell, incentives and subsidies have a function of the first button, which drives greater development.
Classification of Incentives
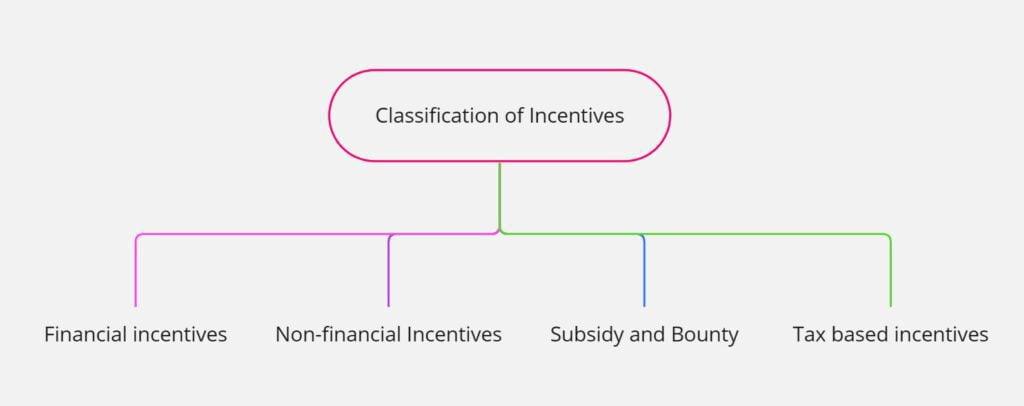
Incentives can be classified in several ways. Incentives are classified in the following ways:
Incentives can be categorized as either financial incentives or non-financial incentives.
Financial incentives
Financial incentives are incentives in terms of money.
Profit Potential
- Building Wealth: Entrepreneurship offers the potential to create significant wealth through building a successful business. This is a major motivator for many, as it allows them to achieve financial independence and security.
- Equity Ownership: Unlike working a traditional job, entrepreneurs own a stake in their business. This means they directly benefit from the company’s profits, providing a strong incentive for growth.
- Control Over Earnings: Entrepreneurs have more control over their income than salaried employees. They can choose to reinvest profits back into the business for growth or take a larger salary as the company matures.
Government Grants and Subsidies
- Reduced Startup Costs: Grants and subsidies can significantly reduce the financial burden of starting a business. This allows entrepreneurs to invest in crucial areas like product development, marketing, and hiring.
- Encouraging Innovation: Governments often target grants towards specific industries or technologies they want to promote. This can be a great advantage for entrepreneurs with innovative ideas in those fields.
- Supporting Underserved Areas: Grants can be used to encourage entrepreneurship in economically disadvantaged areas, fostering job creation and local development.
Tax Breaks
- Lower Tax Burden: Tax breaks can free up significant capital for entrepreneurs. This can be used to fund research and development, hire new employees, or expand into new markets.
- Tax Deductions: Entrepreneurs can often deduct business expenses from their taxable income, further reducing their tax liability. This incentivizes them to invest in equipment, marketing, and other business needs.
- Encouraging Investment: Tax breaks for investors in startups can make them more attractive propositions, increasing access to funding for entrepreneurs.
- Tax breaks for Research and Development (R&D): Tax breaks for R&D are a win-win for startups. They lower costs, allowing startups to invest more in innovation. This financial safety net also encourages risk-taking and helps level the playing field against larger companies. In short, these breaks fuel the growth of innovative startups.
Access to Funding
- Growth Capital: Investors like angel investors, venture capitalists, and banks provide entrepreneurs with the capital needed to grow their businesses beyond bootstrapping. This allows them to scale their operations, hire talent, and pursue new opportunities.
- Validation and Expertise: Securing funding from reputable investors can be a strong validation of an entrepreneur’s idea and business plan. Investors often offer valuable mentorship and expertise alongside financial resources.
- Different Funding Stages: There are various investor types catering to different stages of a business. Angel investors can help with initial funding, while venture capitalists support high-growth companies with significant potential.
Other Considerations
- Financial Risk: Entrepreneurship involves inherent financial risk. While the potential rewards are high, there’s also a chance of failurEntrepreneurs must weigh the risks and rewards carefully.
- Impact Investing: An increasing number of investors are looking to support businesses with a positive social or environmental impact alongside financial returns. This opens up funding opportunities for entrepreneurs with socially conscious ventures.
- Alternative Funding Sources: Crowdfunding platforms and business loans can be alternative sources of funding for entrepreneurs who may not qualify for traditional venture capital investment. Crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo have revolutionized how entrepreneurs raise capital. These platforms allow project creators to pitch their ideas directly to a vast online audience, bypassing traditional gatekeepers like banks or venture capitalists.
Non-financial Incentives
Non-financial incentives and non-monetary incentives such as marketing assistance, technical assistance, etc.
Modern Support Systems:
- Incubators and Accelerators: These programs provide crucial resources like shared workspace, mentorship, and connections to investors.
- Government Mentorship Programs: Many governments connect entrepreneurs with experienced business leaders for guidance.
- Online Learning Platforms: Affordable online courses offer valuable business education and training for aspiring entrepreneurs.
- Coworking Spaces: Shared workspaces provide cost-effective and flexible alternatives to traditional office leases.
- Streamlined Business Permit Processes: Governments are making it easier to navigate the paperwork involved in launching a business.
Emerging Trends
- Coworking spaces have become a game-changer for entrepreneurs. These shared workspaces offer a cost-effective and adaptable solution compared to traditional office leases.
- Entrepreneurs can ditch long-term commitments and enjoy flexible arrangements, scaling their workspace needs up or down as their business grows.
- Beyond affordability, coworking spaces foster a vibrant atmosphere where entrepreneurs can network, collaborate, and share ideas with other like-minded individuals.
- Recognizing this potential, governments are increasingly launching initiatives to streamline the business permit process. This makes it easier for entrepreneurs to navigate the often-daunting paperwork and regulations involved in launching a venture.
- By simplifying the process, governments are helping to cultivate a more entrepreneurial ecosystem, fostering innovation and economic growth.
Be Your Boss:
- Control and Decision-Making: You chart the course! Entrepreneurship empowers you to set your own goals, choose your projects, and define your success.
- Autonomy and Flexibility: Design your work style. Set your hours, create a work environment that inspires you, and manage your time as you see fit.
- Building Your Legacy: The business becomes an extension of yourself. You’ll have the satisfaction of seeing your vision come to life and leaving a lasting mark.
Building Something New:
- Creativity and Innovation: Turn your ideas into reality. Entrepreneurship allows you to experiment, develop new solutions, and disrupt existing markets.
- Making a Difference: Be a positive force for change. You can address social or environmental problems, create jobs, and contribute to a better future.
- The Thrill of the Challenge: There’s immense satisfaction in taking an idea from concept to a tangible product or service that benefits others.
Challenge and Growth:
- Stepping Outside Your Comfort Zone: Entrepreneurship pushes you to constantly learn and adapt. You’ll encounter new challenges, solve complex problems, and develop a diverse skillset.
- Building Resilience: You’ll learn from failures, overcome obstacles, and develop the grit and determination to succeed.
- Personal Growth: The entrepreneurial journey is a catalyst for personal development. You’ll build confidence, sharpen your communication skills, and become a more well-rounded leader.
Flexibility:
- Control Over Your Schedule: Set work hours that fit your life. This is especially appealing to parents, caregivers, or those who value a flexible schedule.
- Location Independence (in some cases): Depending on your business, you might be able to work remotely or from flexible locations, offering greater freedom and lifestyle choices.
- Pursuing Your Passions: Align your work with your interests. Entrepreneurship allows you to turn a passion into a career, adding a deeper sense of purpose to your work.
Other Considerations:
- Recognition and Status: Building a successful business can bring recognition and respect within your industry or community.
- Impact on Others: Entrepreneurs have the power to create jobs, inspire others, and contribute to the economic well-being of their communities.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Overcoming challenges and achieving milestones brings immense satisfaction and a sense of accomplishment.
Subsidy and Bounty.

Incentives can also be classified into concession, subsidy, and bounty.
Concession
Concession means charging lower fees for services to enable the enterprises to compete with others. It is not a lump-sum payment.
Subsidy
The word Subsidy means a one-time payment cum transfer that is granted by the Government to an entrepreneur to support him pay the concluding price. An industry that is deemed crucial for the country’s well-being.
Bounty
The word ‘bounty’ is the name of something that is given by a government to an industry to help it compete with other units in the home market or foreign market. This kindergarten process is done by making the output of one node connect with that node that will be next.
Bounty is different from subsidy. The bounty helps the local industry, while the subsidies are selected to serve the interest of the nation.
Non-tax-based incentives and Tax based incentives
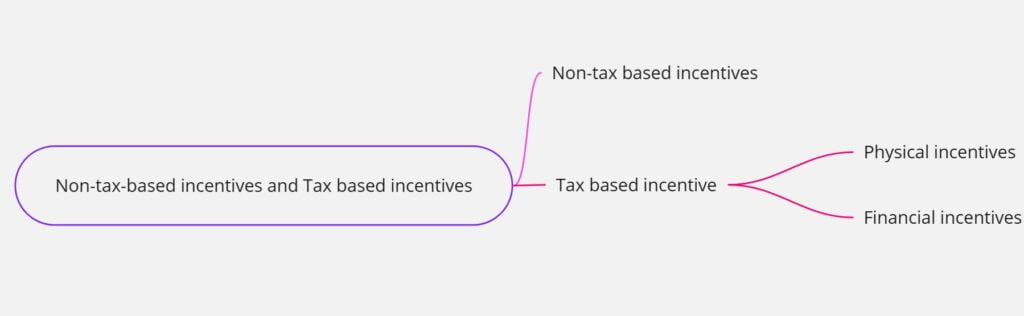
Incentives can also be classified as non-tax-based incentives and tax-based incentives.
Non-tax based incentives
These are incentives that are not based on tax. For example, seed capital assistance, capital investment subsidy, etc.
Tax based incentives
Tax incentives are incentives that are determined by taxes and duties.
Tax-based incentives are again classified into physical incentives and financial incentives.
Physical incentives
These incentives are in the form of exemption, rebate, refund, or postponement of direct or indirect taxes leviable on production or profit. Income tax savings, GST benefits, duty-free imports, etc are examples.
Financial incentives
These include various types of credit facilities at concessional rates, direct and indirect cash subsidies for price advantage, and direct cash subsidies for special promotional efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, incentives for entrepreneurs play an important role in developing entrepreneurial systems. By providing financial and non-financial support, these incentives empower individuals to turn their ideas into reality, contribute to economic growth, and create job opportunities As the business environment evolves, so too and the various incentives offered will continue. Recognizing this, policymakers and organizations should strive to develop comprehensive support systems that foster innovation and empower the next generation of entrepreneurs.











Leave a Review